39 are treasury bills zero coupon bonds
Frequently Asked Questions - U.S. Department of the Treasury The par yield curve is based on securities that pay interest on a semiannual basis and the yields are "bond-equivalent" yields. Treasury does not create or publish daily zero-coupon curve rates. Does the par yield curve only assume semiannual interest payment from 2-years out (i.e., since that is the shortest maturity coupon Treasury issue)? No. Zero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula It is also called a pure discount bond or deep discount bond. U.S. Treasury bills are an example of a zero-coupon bond. Summary A zero-coupon bond is a bond that pays no interest. The bond trades at a discount to its face value. Reinvestment risk is not relevant for zero-coupon bonds, but interest rate risk is relevant for the bonds.
Zero-Coupon Bond Definition - Investopedia Zero-coupon bonds can be issued from a variety of sources, including the U.S. Treasury, state and local government entities, and corporations. Most zero-coupon bonds trade on the major exchanges.
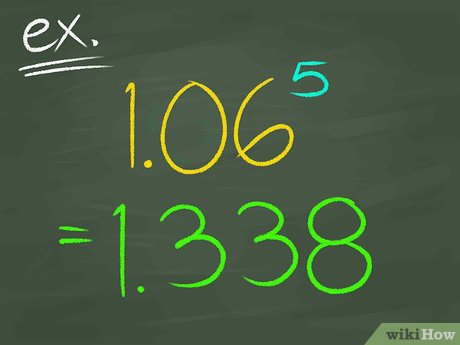
Are treasury bills zero coupon bonds
Understanding Zero Coupon Bonds - Part One - The Balance Zero coupon bonds generally come in maturities from one to 40 years. The U.S. Treasury issues range from six months to 30 years and are the most popular ones, along with municipalities and corporations. 1 Here are some general characteristics of zero coupon bonds: Issued at deep discount and redeemed at full face value U.S. Treasury Bonds, Bills and Notes: What They Are and How to Buy U.S. Treasury bonds are fixed-income securities issued and backed by the full faith and credit of the federal government, which means the U.S. government must find a way to repay the debt. Given ... Should I Invest in Zero Coupon Bonds? | The Motley Fool For instance, a 10-year Treasury bond might have a coupon rate of 3%, meaning that each $1,000 face-value bond will make interest payments totaling $30. For Treasuries, that would come in two...
Are treasury bills zero coupon bonds. › treasury-bills-vs-bondsTreasury Bills vs Bonds | Top 5 Differences (with Infographics) T-bills do not pay any coupon. They are floated as a zero-coupon bond Zero-coupon Bond In contrast to a typical coupon-bearing bond, a zero-coupon bond (also known as a Pure Discount Bond or Accrual Bond) is a bond that is issued at a discount to its par value and does not pay periodic interest. In other words, the annual implied interest payment is included into the face value of the bond, which is paid at maturity. › us-treasury-bondsUS Treasury Bonds - Fidelity The coupon rate is fixed at the time of issuance and is paid every six months. Other Treasury securities, such as Treasury bills (which have maturities of one year or less) or zero-coupon bonds, do not pay a regular coupon. Instead, they are sold at a discount to their face (or par) value; investors receive the full face value at maturity ... Norwegian government securities - Norges Bank The zero coupon yield curve shows an unambiguous relationship between the effective yield (yield to maturity) and term to maturity and is not affected by the fact that individual bonds are issued with differing coupons. The published zero coupon yields are estimated values based on observed effective yields on Norwegian Treasury bills (zero ... Whats The Difference Between A Zero Coupon Bond And A Treasury Bill Why is treasury bill also called as zero coupon bonds . Preview. 5 hours ago 27 answers. 3.2K people helped. A zero coupon bond is a bond which is issued at a price which is less than its face value and, is repaid at its face value on the date of its maturity. Since treasury bills follow this rule, they are also called zero coupon bonds.Niccherip5 and 7 more users found this answer helpful ...
› terms › tTreasury Bills (T-Bills) Definition - Investopedia Jun 02, 2022 · Treasury Bill - T-Bill: A Treasury bill (T-Bill) is a short-term debt obligation backed by the Treasury Dept. of the U.S. government with a maturity of less than one year, sold in denominations of ... Treasury Bills (T-Bills) - Meaning, Examples, Calculations Treasury bills are a type of zero-coupon security where the central government borrows funds from the individual for a period of 364 days or less. In return, the investors receive interest. These money market instruments provide a return on investment at once, and there is no provision for periodic returns. › treasury-bills-vs-bondsTreasury Bills vs Bonds | Top 5 Best Differences (With ... Let us Discussed some of the major differences between Treasury Bills vs Bonds: Treasury bills are short term money market instruments whereas Treasury Bonds are long term capital market instruments. Treasury bills are issued at a discounted price whereas Treasury Bonds pay interest every six months to holders of a bond. Treasury bills mature ... 2 Treasury and are semiannual bonds while Treasury are zero coupon ... 2 Treasury and are semiannual bonds while Treasury are zero coupon instruments A from FIN 3121 at Kazakhstan Institute of Management, Economics and Strategic Research
calculator.me › savings › zero-coupon-bondsZero Coupon Bond Value Calculator: Calculate Price, Yield to ... Disadvantages of Zero-coupon Bonds. There are two major disadvantages of zero-coupon bonds. The first disadvantage is they do not throw off any income as the capital is stored in the bond. In some countries the imputed interest may be taxed as income even though the bond has not yet been redeemed or reached maturity. Domestic bonds: USA, Bills 0% 25nov2022, USD (183D) US912796W704 Zero-coupon bonds, Bills. Issue | Issuer ... It is represented by United States Treasury bonds (issued by the United States Department of the Treasury to finance government spending) and by non-marketable securities. United States Treasury securities include Treasury bills (short-term securities maturing in one year or less at par), Treasury ... › articles › investingAdvantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds Jan 31, 2022 · Zero-coupon U.S. Treasury bonds have a poor risk-return profile when held alone. Long-dated zero-coupon Treasury bonds are more volatile than the stock market, but they offer the lower long-run ... What is zero coupon bonds? - myITreturn Help Center Hence the term is called as zero-coupon bond. When the bond reaches maturity, its investors receive its par (or face) value. Examples of zero-coupon bonds include U.S. Treasury bills, U.S. savings bonds, long-term zero-coupon bonds and any other type of coupon bond that has been stripped of its coupons. Some zero coupon bonds are inflation indexed.
Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Zero coupon bonds are bonds that do not pay interest during the life of the bonds. Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due. The maturity dates on zero coupon bonds are usually long-term—many don't mature for ten, fifteen, or more years.
Zero-coupon bond - Wikipedia A zero coupon bond is a bond in which the face value is repaid at the time of maturity. That definition assumes a positive time value of money. It does not make periodic interest payments or have so-called coupons, hence the term zero coupon bond. When the bond reaches maturity, its investor receives its par value. Examples of zero-coupon bonds include US Treasury bills, US savings bonds, long-term zero-coupon bonds, and any type of coupon bond that has been stripped of its coupons. Zero coupon
What's the difference between a zero-coupon bond and a Treasury bill? T-bills do not pay any coupon. They are floated as a zero-coupon bond to the investors, they are issued at discounts, and the investors receive the face value at the end of the tenure, which is the return on their investment. Bonds pay interest in the form of a coupon to the investors quarterly or semi-annually.
What is Treasury Bill (T-bill)? - Indian Economy Treasury bills are presently issued in three maturities, namely, 91 day, 182 day and 364 day. Treasury bills are zero coupon securities and pay no interest. Rather, they are issued at a discount (at a reduced amount) and redeemed (given back money) at the face value at maturity.
United States Treasury security - Wikipedia Treasury bills (T-bills) are zero-coupon bonds that mature in one year or less. They are bought at a discount of the par value and, instead of paying a coupon interest, are eventually redeemed at that par value to create a positive yield to maturity.. Regular weekly T-bills are commonly issued with maturity dates of 4 weeks, 8 weeks, 13 weeks, 26 weeks, and 52 weeks.
Individual - Treasury Bonds: Rates & Terms Treasury Bonds: Rates & Terms . Treasury bonds are issued in terms of 20 years and 30 years and are offered in multiples of $100. Price and Interest. The price and interest rate of a bond are determined at auction. The price may be greater than, less than, or equal to the bond's par amount (or face value). (See rates in recent auctions.)
Domestic bonds: United Kingdom, Bills 0% 3jan2023, GBP (183D ... Issue Information Domestic bonds United Kingdom, Bills 0% 3jan2023, GBP (183D). Issue, Issuer, Yield, Prices, Payments, Analytical Comments, Ratings. Eng. ... There are also Treasury bills in the country. Treasury bills are zero-coupon eligible debt securities issued by the Debt Management Office. The Government also issues green gilts.
Government - Continued Treasury Zero Coupon Spot Rates* 3.20. 3.38. 3.79. *Four quarters covering calendar year 2012 and the first and second quarters of calendar year 2013 prepared by Economic Policy (EP) using the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) legacy model. Legacy model quarterly rates can be viewed within the "Selected Asset and Liability Price Report" under "Spot (Zero ...
why is treasury bill also called as zero coupon bonds - Brainly.in Treasury notes also referred to as Zero-Coupon Bonds. • They are available for a minimum of and in multiples of that amount. • A treasury bill is a short-term borrowing instrument used by the Indian government that has a maturity of less than a year. • Treasury bills, which are sold to banks and the general public, allow the government to obtain ...
› bills-bonds › treasury-bondsTreasury Bonds | CBK Jun 13, 2022 · five year and fifteen year fixed coupon treasury bonds issue nos. fxd 1/2013/5 & fxd 2/2013/15: 25/03/2013: two year and re-opening of ten year fixed coupon treasury bonds issue nos. fxd 2/2013/2 & fxd 1/2012/10: 25/02/2013: two and fifteen year fixed coupon treasury bonds issue nos. fxd 1/2013/2 & fxd 1/2013/15: 09/01/2013
Zero Coupon Bond Funds: What Are They? - The Balance A zero coupon bond is a bond that doesn't offer interest payments but sells at a discount—a price lower than its face value. 1 The bondholder doesn't get paid while they own the bond, but when the bond matures, they will be repaid the full face value. Zero coupon bond funds are funds that hold these types of bonds.
The One-Minute Guide to Zero Coupon Bonds | FINRA.org Instead of getting interest payments, with a zero you buy the bond at a discount from the face value of the bond, and are paid the face amount when the bond matures. For example, you might pay $3,500 to purchase a 20-year zero-coupon bond with a face value of $10,000. After 20 years, the issuer of the bond pays you $10,000.
14.3 Accounting for Zero-Coupon Bonds - Financial Accounting A zero-coupon bond is one that is popular because of its ease. The face value of a zero-coupon bond is paid to the investor after a specified period of time but no other cash payment is made. There is no stated cash interest. Money is received when the bond is issued and money is paid at the end of the term but no other payments are ever made.
Should I Invest in Zero Coupon Bonds? | The Motley Fool For instance, a 10-year Treasury bond might have a coupon rate of 3%, meaning that each $1,000 face-value bond will make interest payments totaling $30. For Treasuries, that would come in two...
U.S. Treasury Bonds, Bills and Notes: What They Are and How to Buy U.S. Treasury bonds are fixed-income securities issued and backed by the full faith and credit of the federal government, which means the U.S. government must find a way to repay the debt. Given ...
Understanding Zero Coupon Bonds - Part One - The Balance Zero coupon bonds generally come in maturities from one to 40 years. The U.S. Treasury issues range from six months to 30 years and are the most popular ones, along with municipalities and corporations. 1 Here are some general characteristics of zero coupon bonds: Issued at deep discount and redeemed at full face value







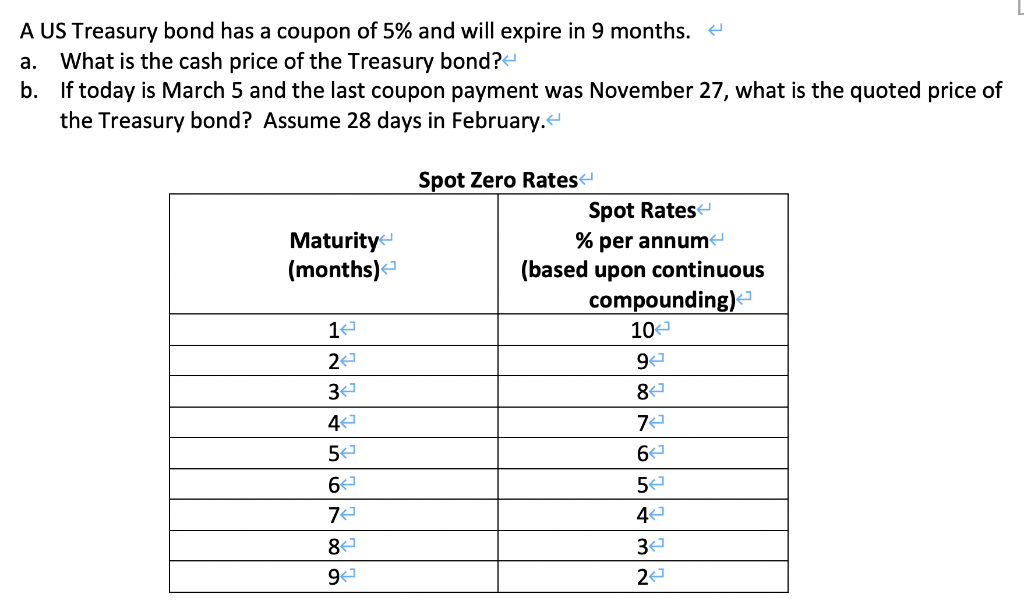






Post a Comment for "39 are treasury bills zero coupon bonds"